l-Asparaginase (l-ASP) is one of the cornerstones of the treatment of paediatric acute lymphoblastic leukaemia (ALL).1 It is used with the aim of depleting circulating asparagine, which induces apoptosis in malignant lymphoid cells indirectly by impeding protein synthesis.2 This systemic depletion of asparagine requires an adequate level of l-ASP activity, which is currently considered to be a level exceeding 100IU/L.3,4
Several l-ASP agents are currently available, each with different pharmacokinetic characteristics. Two are derived from Escherichia coli, including the enzyme in its native form (E. coli-ASP) and the pegylated enzyme (PEG-ASP); and 1 is derived from Erwinia chrysanthemi (Erwinia-ASP). Most current protocols recommend the use of the pegylated enzyme derived from E. coli, while the enzyme derived from Erwinia is used as second- or third-line treatment in cases of hypersensitivity, which develops in up to 22% of patients.5 However, the hypersensitivity reaction is not the only response mediated by the immune system that limits the use of l-ASP, as the phenomenon known as silent inactivation has also been described in the literature (in 8%–10% of cases).2
Our aim in this work was two-fold: on one hand, we sought to demonstrate that routine measurement of l-ASP activity is feasible in everyday clinical practice in hospital settings, and on the other, to present a case that shows that it is possible to use Erwinia-ASP following a hypersensitivity reaction to PEG-ASP and to maintaining adequate activity levels as long as the dosing schedule established for this form of l-ASP is followed rigorously.
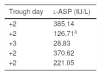
We present the case of a male patient aged 10 years with an ALL diagnosis that was treated according to the United Kingdom Acute Lymphoblastic Leukaemia (UKALL) protocol. At 20 months, the patient experienced a relapse that was treated according to the 2015 LAL/SEHOP-PETHEMA protocol version 1.0 for a first relapse. The patient developed a hypersensitivity reaction following the initial dose of PEG-ASP, so, in adherence to current clinical guidelines, treatment was switched to Erwinia-ASP. Although the source of the protein was different, there was a risk of cross-reactivity that could involve either another hypersensitivity reaction or a silent inactivation of the new form of asparaginase. For these reason, we decided to monitor the levels of asparaginase activity at every through (every 48h, Table 1).
Trough values of plasma l-ASP.
| Trough day | l-ASP (IU/L) |
|---|---|
| +2 | 385.14 |
| +2 | 126.71a |
| +3 | 28.83 |
| +2 | 370.62 |
| +2 | 221.05 |
l-ASP: l-asparaginase.
The patient did not exhibit a hypersensitivity reaction after receiving the first dose of Erwinia-ASP. We only detected a suboptimal level of activity (<100IU/L) in the third through (28.8IU/L), which we attributed to a 24-h delay in the administration of the dose (at 72h instead of 48h) because it was Christmas day. The levels of activity returned to normal in subsequent cycles. Therefore, to date there is no evidence of silent inactivation taking place.
Our results show that Erwinia-ASP can be effective in the treatment of patients that have experienced a hypersensitivity reaction to PEG-ASP. Based on our experience, we can conclude that the use of Erwinia-ASP requires strict adherence to the administration of the drug every 48h to ensure adequate levels of activity. To conclude, we would like to underscore that monitoring these levels makes it possible for clinicians to ascertain the correct use of asparaginase.
Please cite this article as: Viña Romero MM, Gil SG, Casariego GJ, Alonso JM, Nicolás FG. Actividad de Erwinia-asparraginasa tras reacción anafiláctica a Peg-asparraginasa. An Pediatr (Barc). 2019;90:187–188.