Some important factors influencing and maintaining unhealthy habits are food advertising and products accessibility. In order to develop and support recommendations, an analysis of the available evidence on the impact of food advertising on the health of children and adolescents has been carried out.
MethodsLiterature review of systematic reviews and meta-analyses published up to January 2022 for the term “food advertising” that analyzed the impact of food advertising on weight, body mass index (BMI), adiposity, dietary intake, behavior toward the advertised product, its purchase or consumption in children and adolescents.
ResultsTwenty-one systematic reviews fulfilled the inclusion criteria, including a total of 490 primary studies, 5 of which also contained a meta-analysis. The vast majority of the primary studies evaluate intermediate effects, related to the behavior of children and adolescents in relation to advertised products and their consumption. There is great variety in terms of the type of advertising and effects studied. Most of the studies agree that there is an association between food advertising and effect analyzed, being more evident in children under 12 years of age and in obese children. Most recent systematic reviews are focused on online advertising, noticing the negative effects especially in adolescents.
ConclusionsChildren and adolescents are a particularly vulnerable population to food advertising strategies. Despite the difficulty to demonstrate an independent effect, there is evidence of an association between food advertising and childhood and adolescents’ behavior respect to the announced products, and the increase of consumption at short-term. In Spain unhealthy product advertising are still very common in the media and in the children and adolescent's online environment. The Nutrition and Breastfeeding Committee of the Spanish Association of Pediatrics supports the need for regulation and limitation of unhealthy food advertising, covering all media and marketing strategies.
Entre los factores más importantes que influyen en la aparición y el mantenimiento de malos hábitos de alimentación están la accesibilidad y publicidad de los productos alimentarios menos saludables. Con el objetivo de elaborar y fundamentar recomendaciones, se ha realizado un análisis de la evidencia disponible sobre el impacto de la publicidad de alimentos en la salud de niños y adolescentes.
MétodosSe ha realizado una revisión bibliográfica de revisiones sistemáticas y metanálisis publicados hasta enero de 2022 con el término “food advertising”, incluyendo aquellas que analizaban el impacto de la publicidad de alimentos sobre el peso, índice de masa corporal (IMC), adiposidad, ingesta dietética, conducta ante el producto anunciado, su compra o su consumo en niños y adolescentes.
ResultadosFueron incluidas 21 revisiones sistemáticas que incluyen un total de 490 artículos, 5 de las cuales contienen además un meta-análisis. La gran mayoría de los estudios primarios evalúan efectos intermedios, relacionados con el comportamiento de niños y adolescentes ante los productos anunciados y su consumo. Existe gran variedad en cuanto al tipo de publicidad y efectos estudiados. La mayoría de trabajos muestra una asociación entre el tipo de publicidad y el efecto concreto analizado, siendo más evidente en menores de 12 años y en niños obesos. Las revisiones más recientes se centran en la publicidad online indicando sus efectos nocivos especialmente en adolescentes.
ConclusionesLos niños y adolescentes constituyen una población especialmente vulnerable. A pesar de la dificultad para demostrar un efecto independiente, hay evidencia de asociación entre la publicidad y los comportamientos en la infancia y adolescencia respecto a los productos anunciados y el aumento de su consumo a corto plazo. En España, los anuncios de productos no saludables siguen muy presentes en los medios y en el entorno online de los menores. El Comité de Nutrición y Lactancia Materna de la Asociación Española de Pediatría suscribe la necesidad de una regulación y limitación de la publicidad de alimentos no saludables que abarque todos los medios y todas las estrategias de marketing.
Childhood overweight and obesity are a global health problem. The term “obesogenic environment” encompasses the factors that determine and influence its pathogenesis. For decades, the foods with an inadequate nutrient profile have become increasingly available, accessible and advertised, contributing to the acquisition and maintenance of poor dietary habits.1 This is particularly important in the case of children and adolescents, as they are a vulnerable population. Food preferences are developed in these stages of life, especially in younger children, shaping their future habits.
Advertisements are currently ubiquitous in everyday life and play an important role in the flow of commercial activity.2 Controversy emerges when what is being advertised could be considered deleterious for the common or individual good. Unhealthy diets are characterised by the habitual consumption of specific food products that share certain characteristics as regards composition, palatability and accessibility. These products can not only directly harm health, but may strongly contribute to displacing consumption of healthier foods.3 Thus, it is a challenge to develop classification criteria beyond the analysis of nutrient composition to identify this type of products.
There is a broad variety of marketing strategies, with technical and psychological characteristics that drive their ability to influence food preferences in the paediatric population.4 Emotional appeals may have to do with fun, happiness, success, social acceptance, skills, physical attractiveness, etc. Usually, emotional appeals are more frequent the lower the nutritional value of the advertised food product.5 The appeal of the product itself, especially in the case of unhealthy foods, is promoted with nutritional claims, highlighting its ability to improve health or provide energy or specific healthy nutrients, usually focusing on a particular characteristic that is isolated from the nutritional value of the whole product. In 2015, approximately 50% of food commercials in Spanish television included some form of nutritional claim, and nearly two thirds were advertising unhealthy products.6 Visual appeals are also frequent, especially the use of cartoon or real-life characters (celebrities) to facilitate the identification of the consumer with the brand7 and develop loyalty to the product. One of the main objectives of marketing targeted to the paediatric population is to induce children and adolescents to demand that their parents purchase the advertised product.8 This demanding, which can reach the level of pestering, is perceived by parents as a significant barrier to making more appropriate choices for their children’s nutrition.9
Television (TV) has been the medium in which children have been most frequently exposed to food advertising, given that in Spain, children aged 4–12 years are likely to watch a mean of 18.8 food or beverage commercials on TV, out of which nearly two thirds are for unhealthy products.10 Most advertised foods and products are unhealthy. However, in recent years, there has been a substantial increase in the use of different online media and social networks by children and adolescents, and therefore of the media in which marketing messages can be delivered. Marketing strategies have adapted to the emerging media to make use of this opportunity.11 Unhealthy products continue to be advertised most frequently, independently of the type of social media.12 The investment in online advertising of foods with high fat, salt or sugar (HFSS) contents has also been growing, to up to 45% of the total budget in 2018.13 Marketing messages are no longer only passive, but may actively engage the users of different online platforms or games. Games can contain advertisements with which the user can interact, or users can be encouraged to share contents of a given brand with their friends.14,15 Similarly, videos published by popular youtubers or influencers can feature images of unhealthy foods or drinks, a strategy that is particularly effective on adolescents.16–19
Childhood is a stage in which individuals are particularly vulnerable to the effects of advertising. Companies use strategies targeted to minors to draw their interest, in some cases quite evident,20 but not so much in others. Cognitive control is not fully developed until early adulthood. There is evidence that when children and adolescents are exposed to visual stimuli related to food, important areas in the brain associated with cognitive control are not activated, which reflects a lesser ability to inhibit the responses to food-related stimuli or images, especially in minors with excess weight.21 Their ability to differentiate an advertisement from other types of content is limited (it starts from age 7–8 years) and it is not fully developed until the end of adolescence, so that they tend to interpret advertising as objective content.21,22 In digital environments, minors may have more difficulty recognising when they are being exposed to advertising, especially when it comes to adolescents and marketing content conveyed through social media. Socially disadvantaged groups and ethnic minorities are most vulnerable to the effects of advertising in their environment.23,24
Broadly speaking, advertising is considered effective in shaping dietary habits in minors, which is the very reason marketing exists and explains the substantial resources the food industry devotes to it. Therefore, advertising could contribute to overweight and obesity. In this document, we analyse the available evidence on the subject.
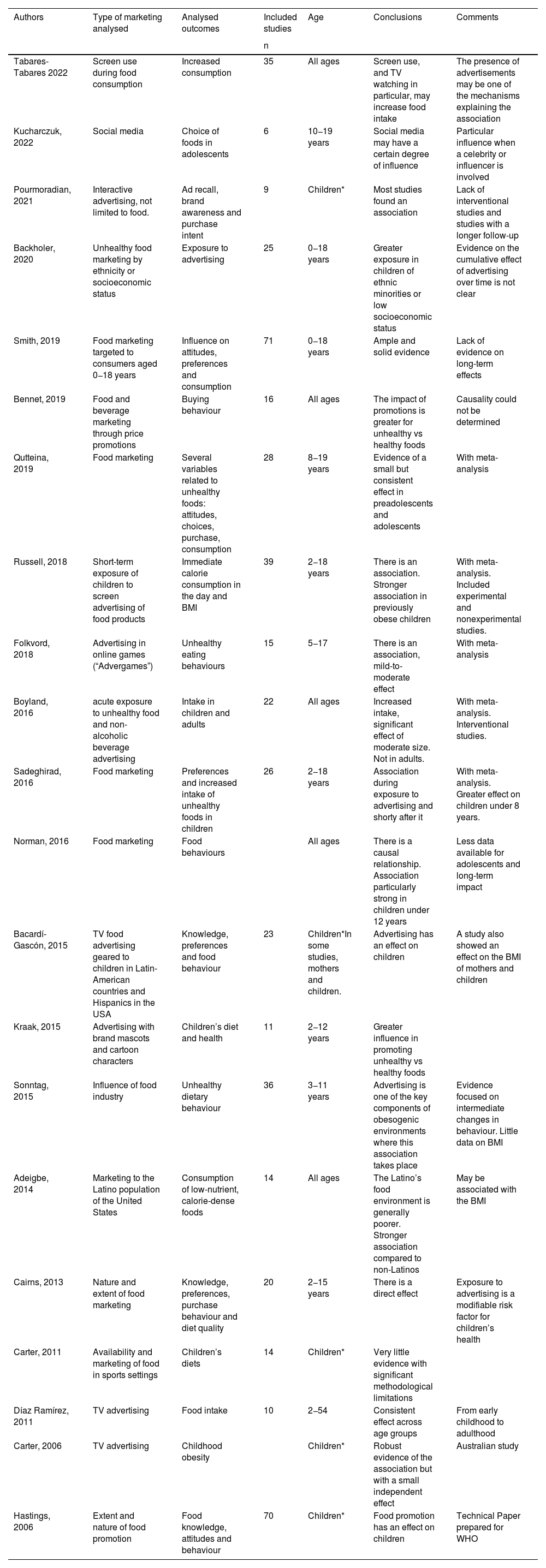
Evidence on the impact of advertising on children and adolescentsTo find evidence to develop and support recommendations on this subject, we conducted a literature search in the PubMed, Cochrane Library and Embase databases for systematic reviews and meta-analysis published in English through January 2022 using the search term “food advertising”, in addition to searching for additional sources in the reference sections of the works identified in the database search. Out of a total of 80 results, we selected articles that analysed the impact in children and adolescents of food advertising in relation to weight, body mass index (BMI), body fat, dietary intake, behaviour towards the advertised product and the purchase or consumption of the advertised product. Table 1 summarises the characteristics and conclusions of the 21 systematic reviews selected in the search,14,15,18,20,23–39 which in turn included a total of 490 articles. Five of them also performed a meta-analysis of the primary sources.15,28–31 Sixteen included studies conducted exclusively in children or adolescents of different age ranges, and the rest included studies in the overall population, including adults.24,25,27,30,32 Most primary sources analysed intermediate effects concerning the behaviour towards advertised products and their consumption. Less frequently, studies analysed the advertising of unhealthy foods and their association with changes in anthropometric values such as the BMI. There was substantial variation in the types of advertising and specific outcomes analysed. All of this complicates the comparison of the findings of different studies.
Systematic reviews on the impact of food and beverage marketing.
| Authors | Type of marketing analysed | Analysed outcomes | Included studies | Age | Conclusions | Comments |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| n | ||||||
| Tabares-Tabares 2022 | Screen use during food consumption | Increased consumption | 35 | All ages | Screen use, and TV watching in particular, may increase food intake | The presence of advertisements may be one of the mechanisms explaining the association |
| Kucharczuk, 2022 | Social media | Choice of foods in adolescents | 6 | 10−19 years | Social media may have a certain degree of influence | Particular influence when a celebrity or influencer is involved |
| Pourmoradian, 2021 | Interactive advertising, not limited to food. | Ad recall, brand awareness and purchase intent | 9 | Children* | Most studies found an association | Lack of interventional studies and studies with a longer follow-up |
| Backholer, 2020 | Unhealthy food marketing by ethnicity or socioeconomic status | Exposure to advertising | 25 | 0−18 years | Greater exposure in children of ethnic minorities or low socioeconomic status | Evidence on the cumulative effect of advertising over time is not clear |
| Smith, 2019 | Food marketing targeted to consumers aged 0−18 years | Influence on attitudes, preferences and consumption | 71 | 0−18 years | Ample and solid evidence | Lack of evidence on long-term effects |
| Bennet, 2019 | Food and beverage marketing through price promotions | Buying behaviour | 16 | All ages | The impact of promotions is greater for unhealthy vs healthy foods | Causality could not be determined |
| Qutteina, 2019 | Food marketing | Several variables related to unhealthy foods: attitudes, choices, purchase, consumption | 28 | 8−19 years | Evidence of a small but consistent effect in preadolescents and adolescents | With meta-analysis |
| Russell, 2018 | Short-term exposure of children to screen advertising of food products | Immediate calorie consumption in the day and BMI | 39 | 2−18 years | There is an association. Stronger association in previously obese children | With meta-analysis. Included experimental and nonexperimental studies. |
| Folkvord, 2018 | Advertising in online games (“Advergames”) | Unhealthy eating behaviours | 15 | 5−17 | There is an association, mild-to-moderate effect | With meta-analysis |
| Boyland, 2016 | acute exposure to unhealthy food and non-alcoholic beverage advertising | Intake in children and adults | 22 | All ages | Increased intake, significant effect of moderate size. Not in adults. | With meta-analysis. Interventional studies. |
| Sadeghirad, 2016 | Food marketing | Preferences and increased intake of unhealthy foods in children | 26 | 2−18 years | Association during exposure to advertising and shorty after it | With meta-analysis. Greater effect on children under 8 years. |
| Norman, 2016 | Food marketing | Food behaviours | All ages | There is a causal relationship. Association particularly strong in children under 12 years | Less data available for adolescents and long-term impact | |
| Bacardí-Gascón, 2015 | TV food advertising geared to children in Latin-American countries and Hispanics in the USA | Knowledge, preferences and food behaviour | 23 | Children*In some studies, mothers and children. | Advertising has an effect on children | A study also showed an effect on the BMI of mothers and children |
| Kraak, 2015 | Advertising with brand mascots and cartoon characters | Children’s diet and health | 11 | 2−12 years | Greater influence in promoting unhealthy vs healthy foods | |
| Sonntag, 2015 | Influence of food industry | Unhealthy dietary behaviour | 36 | 3−11 years | Advertising is one of the key components of obesogenic environments where this association takes place | Evidence focused on intermediate changes in behaviour. Little data on BMI |
| Adeigbe, 2014 | Marketing to the Latino population of the United States | Consumption of low-nutrient, calorie-dense foods | 14 | All ages | The Latino’s food environment is generally poorer. Stronger association compared to non-Latinos | May be associated with the BMI |
| Cairns, 2013 | Nature and extent of food marketing | Knowledge, preferences, purchase behaviour and diet quality | 20 | 2−15 years | There is a direct effect | Exposure to advertising is a modifiable risk factor for children’s health |
| Carter, 2011 | Availability and marketing of food in sports settings | Children’s diets | 14 | Children* | Very little evidence with significant methodological limitations | |
| Díaz Ramírez, 2011 | TV advertising | Food intake | 10 | 2−54 | Consistent effect across age groups | From early childhood to adulthood |
| Carter, 2006 | TV advertising | Childhood obesity | Children* | Robust evidence of the association but with a small independent effect | Australian study | |
| Hastings, 2006 | Extent and nature of food promotion | Food knowledge, attitudes and behaviour | 70 | Children* | Food promotion has an effect on children | Technical Paper prepared for WHO |
The 5 reviews with meta-analysis concluded that there is an association between advertising and the analysed outcome. Three of the meta-analysis analysed the effect of exposure to advertising of unhealthy foods on the intake of children and adolescents.29–31 In the 2–18 years age group, energy intake increased by 30.4–60kcal during or after exposure in the subset exposed to this kind of advertising compared to the subset without exposure, in addition to an increased likelihood to choose the advertised foods or beverages in the exposed group. The meta-analysis of Russel et al29 also found that the increase in intake was significantly greater in children with overweight or obesity compared to children with normal weight (mean difference, 125.5kcal). Another meta-analysis studied the impact of media food marketing on food-related cognitions, attitudes and behaviours in preadolescents and adolescents,28 and found a significant, although small, effect on outcomes associated with a poor diet, such as greater advertisement recall and more positive attitudes towards unhealthy foods or specific brands, an increase in the intent to buy or demanding the purchase of the products and also negative attitudes towards healthy foods.
Although there is disagreement as regards the strength of the association,27,36 Norman et al32 analysed the impact of advertising in eating behaviours applying the Bradford Hill criteria (developed to determine whether it is appropriate to infer causality in an observed association), and concluded that there was a causal association between them, with a particularly strong association in children aged less than 12 years. Overall, there are fewer data on adolescents, although the reviews agree that adolescence is also stage when the individual is vulnerable to the influence of advertising.14,18,28,32,37 Boyland et al. concluded that the influence of marketing on consumption was significant, even if the size of the effect was small to moderate, as the impact of small effects at the individual level can become important at the level of the population.30 The global increase in the prevalence of obesity is, after all, the result of relatively small but cumulative changes in total energy intake at the individual level.
There is considerable heterogeneity in terms of the type of marketing analysed (TV, use of cartoons or mascots, specific populations or social groups, specific online media). Three reviews focused specifically on the effects of unhealthy food advertising on TV,33,37,38 and found an association with different outcomes in the populations under study (increase in BMI, increased consumption and food preferences). The most recent reviews have analysed the impact of unhealthy food marketing in online media,15,18,25,26 highlighting that it is greater on adolescents.
The evidence published to date has mostly focused on short-term outcomes associated with behaviour, preferences, purchase and consumption of the product or dietary changes within a limited timeframe. Due to methodological difficulties, very few studies have analysed long-term effects and changes in weight, BMI or body fat, and it is generally assumed that changes in in intermediate indicators (such as an increased preference for specific products or their purchase) are a necessary step preceding weight change in children.34 In 2018 Norman et al. analysed whether the immediate effect on consumption of advertising in children aged 7–12 years was compensated in subsequent meals through a decrease in intake. All participants consumed more snacks after the exposure and there was no compensation later on, so the total daily energy intake increased. On the other hand, in real life, there is constant exposure to marketing through different media, and this ongoing exposure would contribute to the persistence and amplification of short-term effects, leading to a sustained impact in terms of BMI increases.30
Sedentary lifestyles are associated with excess weight, but the potential role of the use of electronic devices and their contents (including advertising) in this reduction in physical activity is not clear. Some authors have argued that the sedentary behaviours associated with TV watching do not seem sufficient to justify the increase in childhood obesity, and that the latter may depend more on dietary intake than decreases in physical activity.25 Other authors have found an effect associated with screen use independently of advertising content, not only due to inactivity in itself, but also to the effects of being distracted from the feeling of satiety and other cues that regulate intake.25 As regards marketing in emerging digital media, such as social networks or interactive online games, there are very few studies, and their results are inconclusive,28,29,31 although some suggest that its impact may be greater than the impact of advertising on TV.12,15
In light of the above, there is sufficient evidence to state that advertising has an independent effect on the development of obesity, although further studies are required to determine the magnitude of this effect, particularly in the long term.
Regulation of advertising in Spain and internationallyIn 2010, the WHO published recommendations on the marketing of foods and non-alcoholic beverages to children, calling governments to act to reduce its impact by reducing both the exposure to marketing and its “power” or persuasive capacity. In 2018, the implementation of these recommendations was assessed, and significant gaps were identified, underscoring the need to improve adherence. The European Union considers the evidence on the exposure of children to food marketing, especially online, “alarming”, and has urged the member states to implement initiatives to reduce its pressure (EU 2018/1808).
Few countries have regulations that legally restrict food advertising to children, and in most cases restrictions or bans are limited to television during children’s programming. Most countries either have no regulation on the subject or have established self-regulation codes (commitment of the food industry to self-impose restrictions to reduce the exposure to and impact of food advertising targeting children). In 2005, Spain instituted the code for the self-regulation of food and drink advertising targeting minors, the prevention of obesity and health (PAOS code), an agreement between the Agencia Española de Seguridad Alimentaria y Nutrición (AESAN, Spanish Agency of Food Safety and Nutrition) and food marketing agencies meant to limit exposure of children to advertising of foods and beverage with a high fat, sugar or salt content. At the time, our Committee on Nutrition underscored its importance for the prevention of childhood obesity. After 16 years of experience, the conclusion is that the effectiveness of industry self-regulation measures is poor.10,5,33 In fact, the nutrient profile of the foods advertised in Spanish TV channels worsened between 2013 and 2018, and out of the 300 advertising campaigns most frequently seen on television by Spanish children aged 4–12 years in the 2016–2018 period, only 21% advertised food with a high or medium nutritional value.40 On the other hand, in a resolution approved in October 2018, the WHO called for the engagement of the private sector for advancing health. Governmental and public health authorities must prioritise the protection of children on account of their vulnerability, which limits the right of corporations to advertise their products.
The barriers that hinder the ability of families to choose healthier foods are not limited to the marketing of unhealthy foods, but also to the availability and pricing of these products. Mere information about foods or knowledge about nutrition are not enough to guarantee an improvement in the choices made by families, so it is also necessary to regulate advertising through legislation. Furthermore, it would be unfair to put the onus on families to make healthy dietary choices for children, with the rationale that they are free to do so, given how difficult it can be to make these choices in the present obesogenic environment.
The regulation of advertising targeting minors is included in nearly every global proposal aimed at reducing the prevalence of obesity. There is sufficient evidence on the poor efficacy of voluntary self-regulation by the food industry, but there is still little evidence on the effectiveness of governmental policies aimed at limiting the influence of marketing. Nevertheless, despite instances in which restrictive policies have failed, most experiences have been positive. These policies can have a direct effect by reducing the number of broadcast commercials and also of sales. In most of the published studies and reviews on the subject, the authors clearly recommend implementing measures to protect minors beyond self-regulation strategies.27,30 The potential health benefits of eliminating advertising of unhealthy foods could pay off in terms of cost-effectiveness. Although it is believed that restrictions focused on the prime time of children’s programming are the easiest way to limit exposure, policies would be more effective if their scope broadened to include all types of marketing, all types of media and the adolescent population, and imposing regulations not only on the amount of advertising, but also on the persuasive techniques used in marketing.15
Limitations and future challengesIt is difficult to isolate the effects of advertising from other factors that could influence food purchase and consumption behaviours and changes in weight, BMI or body fat. Performance of more interventional studies with a longer follow-up could help ascertain whether the changes observed in the short term in intermediate indicators are actually a necessary intervening step for the subsequent increase in BMI. The challenge is to continue investigating the specific impact of food advertising that reaches minors through new technologies. The current evidence on the effectiveness of different measures and policies aimed at reducing the impact of food advertising on the health of children and adolescents is scarce.35 New data would help guide legislators, focus more accurately on key aspects and improve the impact on choices.
ConclusionAt present, overweight and obesity are a global health problem. Their high prevalence is associated with changes in lifestyles, lack of adherence to healthy traditional diets and an increase in sedentary habits. Furthermore, the consumption of unhealthy foods by children and adolescents is promoted by marketing campaigns. Research has shown an association between advertising, the behaviour of children and adolescents toward advertised products (recall, preference, purchase) and their consumption of these products in the short term. Due to the difficulties involved in the development of specific studies with long enough follow-up periods, the evidence on the long-term impact of advertising is more limited.
Position of the Committee- -
Children and adolescents are a subset of the population that is particularly vulnerable to advertising and marketing strategies aimed at developing brand loyalty to specific foods or drinks, and therefore should be protected.
- -
Children and adolescents are exposed to advertising of unhealthy foods and drinks through television and/or electronic devices with an internet connection, and the impact of this exposure is associated to screen time.
- -
There is evidence of an association between the advertising of unhealthy foods and drinks, the behaviour of children and adolescents toward the advertised products (recall, preference, purchase) and increased consumption of these products.
- -
The WHO and the EU have urged countries to protect minors from the effects of unhealthy food advertising. Turning over this responsibility to the industry through self-regulation agreements has not proven very effective.
- -
Although attempts have been made in Spain to regulate food advertising targeting children (PAOS Code), advertisements of unhealthy foods continue to be ubiquitous in broadcasting and online media consumed or used by children.
- -
The Committee on Breastfeeding and Nutrition of the AEP endorses the need to set limits to unhealthy food advertising that targets children and adolescents encompassing every type of media and marketing strategy.
Please cite this article as: Rodríguez Delgado J, Campoy C, Martínez RG, Mayo EG, Gil-Campos M, Jiménez DG, et al. Publicidad de alimentos no saludables. posicionamiento del comité de nutrición y lactancia materna de la Asociación Española de Pediatría. An Pediatr (Barc). 2022;97:206–206.