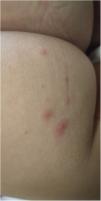
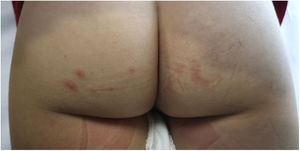
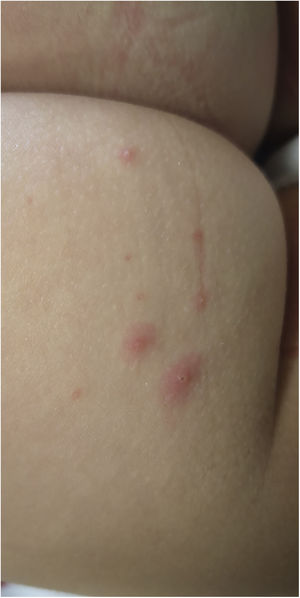
We present the case of a girl aged 3 years brought in for observation of cutaneous lesions in the absence of fever, pruritus or other symptoms. The salient feature in the physical examination was the presence polymorphous cutaneous lesions localised to the buttocks, with umbilicated pustular, vesicular and papular elements and a maximum diameter of 3 mm (Figs. 1 and 2). There was no evidence of oral, perianal or genital lesions. There was also no significant lymph node or visceral organ enlargement, and the rest of the examination was normal. A few hours earlier, monkeypox virus (MPXV) infection had been confirmed in the father. The patient had no history of travel or contact with animals. Testing by of a vesicular fluid swab specimen turned out positive for MPXV (real-time polymerase chain reaction). Instructions were given to have the patient isolate at home with use of contact, airborne and droplet precautions until the full resolution of the cutaneous lesions (at 10 days from onset). At the 2-month follow-up, there were no complications and new lesions had not developed. Additional cases had not been detected in any contacts in the school.
Detail of cutaneous lesions in Fig. 1.
This is the first paediatric case of MPXV infection reported in Spain (June 17, 2022).
Monkeypox is a viral zoonosis produced by MPXV, which has become the most important Orthopoxvirus species worldwide.1 At present, numerous outbreaks have been identified in different countries, with more than 2000 cases reported in Spain as of July 2022. The severity of the infection depends on the presence of comorbidities and age, with a reported overall mortality of 15% and a higher risk in young children in endemic areas in sub-Saharan Africa.2
It produces symptoms similar to those observed in patients with smallpox, although less severe. The main mechanism of transmission in humans is through contact with mammals, chiefly rodents or primates, in endemic regions. Transmission from one person to another is also possible through air droplets, direct contact with cutaneous lesions, bodily fluids or objects used by infected individuals.1 The most frequent mechanism of transmission in the current outbreak has been sexual contact.
Infection by MPXV tends to cause mild and self-limiting disease lasting 2–4 weeks that only requires symptomatic treatment. However, in some cases it may cause severe disease. Complications can include bacterial superinfection of the cutaneous lesions, bronchopneumonia, sepsis, encephalitis and keratitis. Isolation measures are indicated, with contact, airborne and droplet precaution, until the full resolution of the cutaneous lesions. Antiviral drugs, such as brincidofovir and tecovirimat, have been tried in humans, but there is not enough evidence yet to support the indication.3 Post-exposure prophylaxis with intravenous immunoglobulin or smallpox vaccine is not approved in the paediatric age group, and should be reserved for compassionate use.4 Whenever a case is confirmed, close contacts should be followed up, especially any sexual contacts, for 3 weeks.