Mayer-Rokitansky-Küster-Hauser (MRKH) syndrome is characterised by congenital aplasia of the uterus and the upper 2/3 of the vagina in women showing normal development of secondary sexual characteristics and a normal 46, XX karyotype.1 Its estimated incidence is of 1 in 4000–5000 live female births.2 Jarcho-Levin syndrome (JLS) or spondylocostal dysostosis is defined by the association of costal and vertebral malformations resulting in a shortened trunk and short stature.3 It occurs in 1 out of 4000 live births.4 Here, we present the case of a female patient with a neonatal diagnosis of JLS who sought care for primary amenorrhoea, the evaluation of which revealed Müllerian agenesis.
The patient was a girl aged 15 years with a diagnosis of primary amenorrhoea. The prenatal history was unremarkable. She received a diagnosis of JLS at birth based on the presence of a shortened trunk and thoracolumbar malformations. The patient also had a perimembranous ventricular septal defect, an ostium secundum atrial septal defect and a right inguinal hernia containing the right ovary.
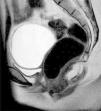
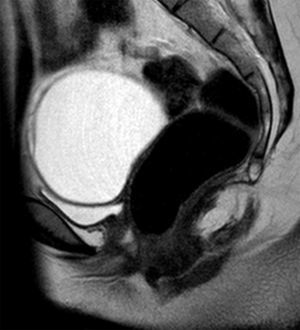
At the time of assessment she had completed puberty (Tanner stage V) with normal female genitalia. We did not observe any signs of hyperandrogenism. A pelvic ultrasound scan, bone age study and measurement of hormone levels were requested for evaluation of the primary amenorrhoea. The ultrasound examination found no evidence of a uterus or ovaries. The bone age was consistent with the chronological age. The levels of estradiol (92ng/mL) and gonadotropins (luteinising hormone, 13.1mIU/mL and follicle-stimulating hormone, 4.6mIU/mL) were in the normal range. The patient underwent magnetic resonance imaging of the abdomen and pelvis (Fig. 1), which found that the uterus and the upper third of the vagina were absent. The ovaries were in the normal location, with detection of a cyst in the right one. The morphology and position of the kidneys were normal.
These findings led to the diagnosis of MRKH syndrome, of which there are 2 types: type I (OMIM 277000), with isolated aplasia of the uterus and vagina, and type II (OMIM 601076), which, as occurred in the case presented here, is associated with other congenital anomalies, usually involving the kidneys, heart, skeleton, and hearing defects. At the skeletal level, the literature describes malformations of the spine (isolated, scoliosis, Klippel-Feil), ribs, palate or extremities.1
Since the involved organ systems have a common mesodermal origin and are closely related during embryogenesis, it has been proposed that the changes leading to MRKH syndrome occur in the very early stages of development. The presence of cases with different degrees of involvement in the same family has led to the investigation of candidate genes, such as those encoding anti-Müllerian hormone (AMH) and its receptor, Wt1, PAX2, HOX homeobox genes and WNT, but a causal relationship with the disorder has not been found. There are reports of cases of MRKH syndrome type II associated with hyperandrogenism in patients with mutations in the WNT4 gene.1,5 At the same time, JLS has been linked to mutations in gene DLL3, which is part of the Notch signalling pathway involved in embryogenesis.3 The presence of different loci in these genes that could be related to both diseases suggests that in this case the aetiology was multifactorial, polygenic or involved defects in several common signalling pathways.
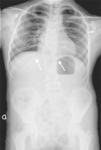
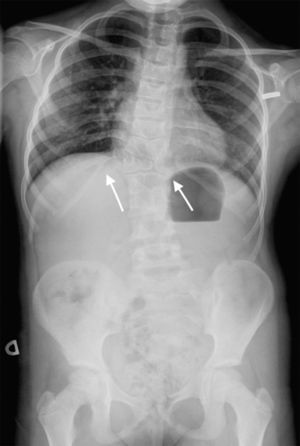
The initial diagnosis in our patient was JLS on account of the presence of shield chest, T12 butterfly vertebra, L1-L2-L3 fused vertebrae, and costal anomalies (fused right 11th and 12th ribs and absence of 1st right rib) (Fig. 2). Later on, she received the additional diagnosis of MRKH syndrome due to the absence of the uterus and upper portion of the vagina. At present, the patient has non-progressive scoliosis with 45° of curvature in the dorsal spine and a moderate restrictive ventilatory defect, and has no residual cardiac lesions. She remains in multidisciplinary followup.
Women with MRKH syndrome can only have children through adoption, surrogacy or uterus transplantation. A child was born alive for the first time after a uterus transplantation in 2014.6 On the other hand, there is a growing interest in the use of bioengineering to treat female infertility through the potential development of replacement tissues and organs, which among other advantages would circumvent the need for immunosuppression.
Our aim in this article is to present the first case of an association between MRKH syndrome and JLS.
Although there are reports of vertebral and/or costal anomalies in association with MRKH syndrome, we did not find any cases associated with JLS or spondylocostal dysostosis in the reviewed literature. Similarly, the literature describes some cases of JLS associated with urogenital malformation, but none meeting the diagnostic criteria for MRKH syndrome.
In our patient, skeletal and cardiac malformations were detected early, but the diagnosis of MRKH syndrome was delayed, something that could be avoided by performing a complete screening for other anomalies.
Please cite this article as: Barriga Buján R, Muinelo Segade A, Prado-Carro A, González Herranz P, Soler Fernández R. Síndromes de Jarcho-Levin y Rokitansky. Una excepcional asociación. An Pediatr (Barc). 2018;88:169–171.