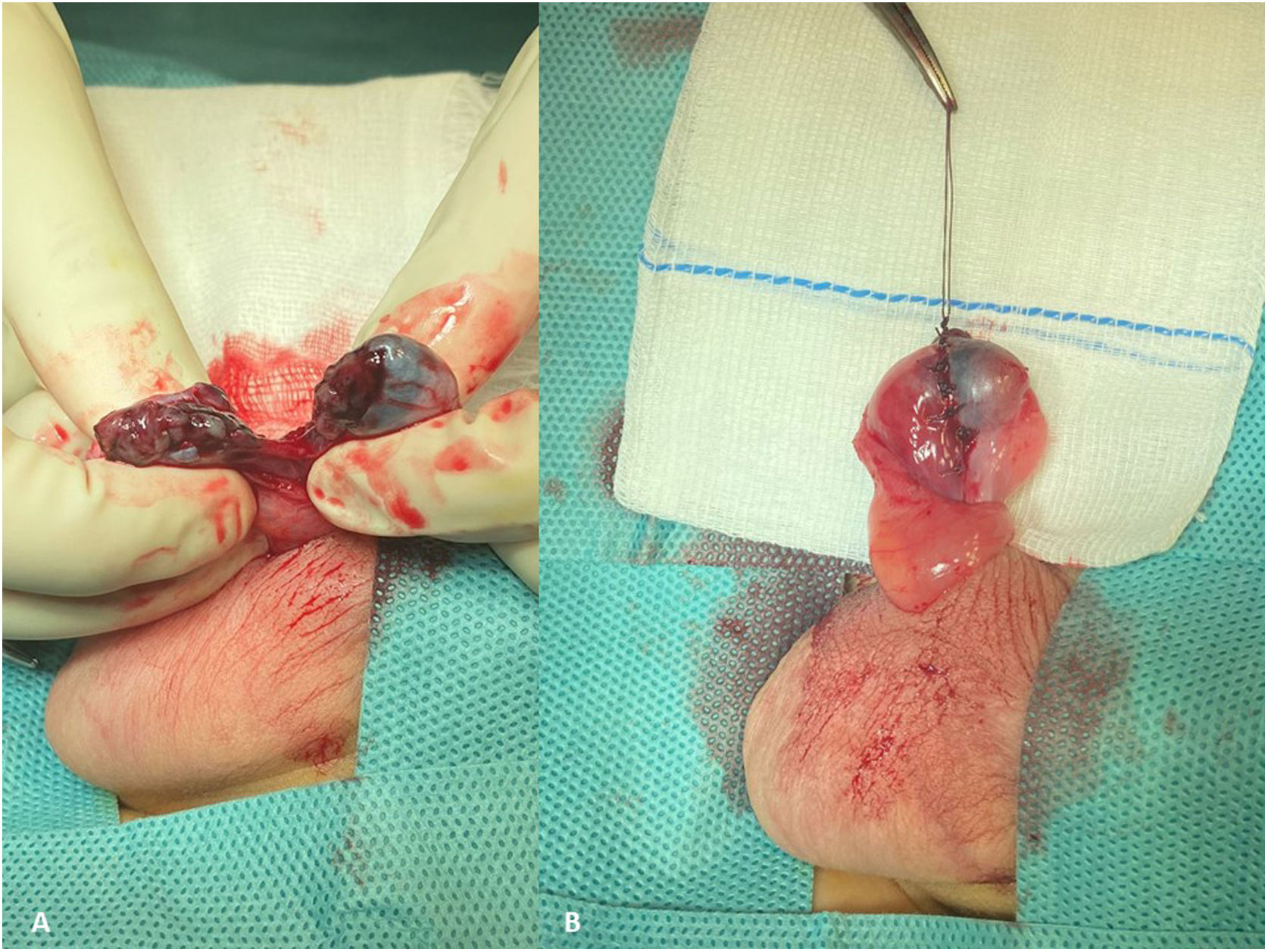
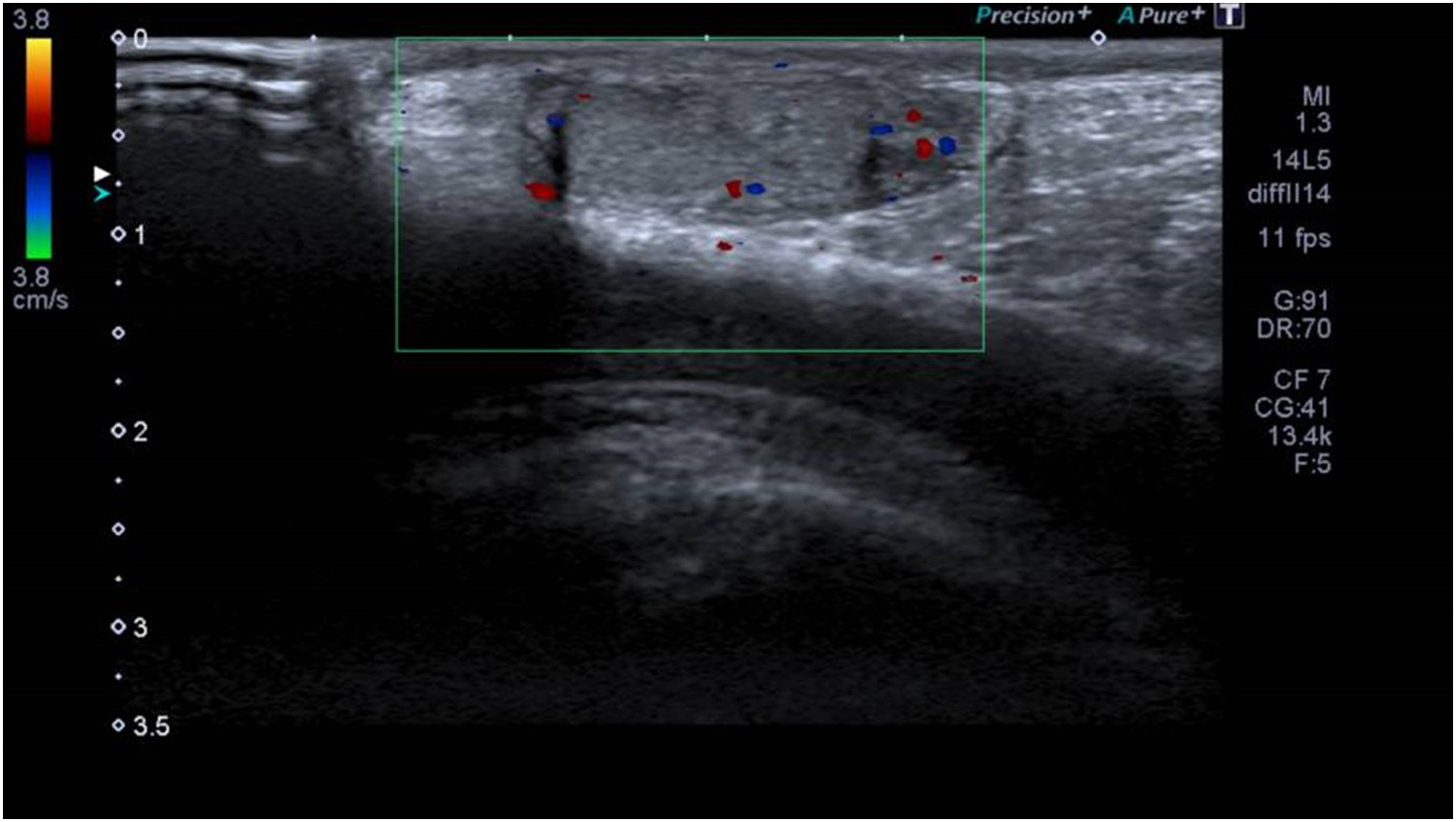
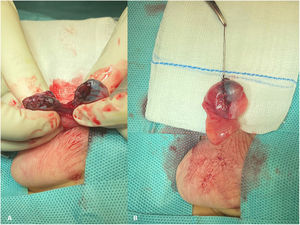
A boy aged 10 years presented to the emergency department with right testicular pain with onset 2 h prior after experiencing direct trauma playing soccer. The physical examination revealed increased volume in the right hemiscrotum, severe pain in the right testicle on palpation, an irregular outline and no abnormalities on transillumination. The features of the scrotal ultrasound were compatible with right testicular rupture (Fig. 1). Urgent surgery was performed. The procedure evinced complete rupture of the right testicle and epidydimal body. Surgical repair was performed with resorbable materials (Fig. 2). The postoperative outcome was favourable and the patient was discharged in 24 h. At 1 year of follow-up, the right testicle is considered viable (Fig. 3).
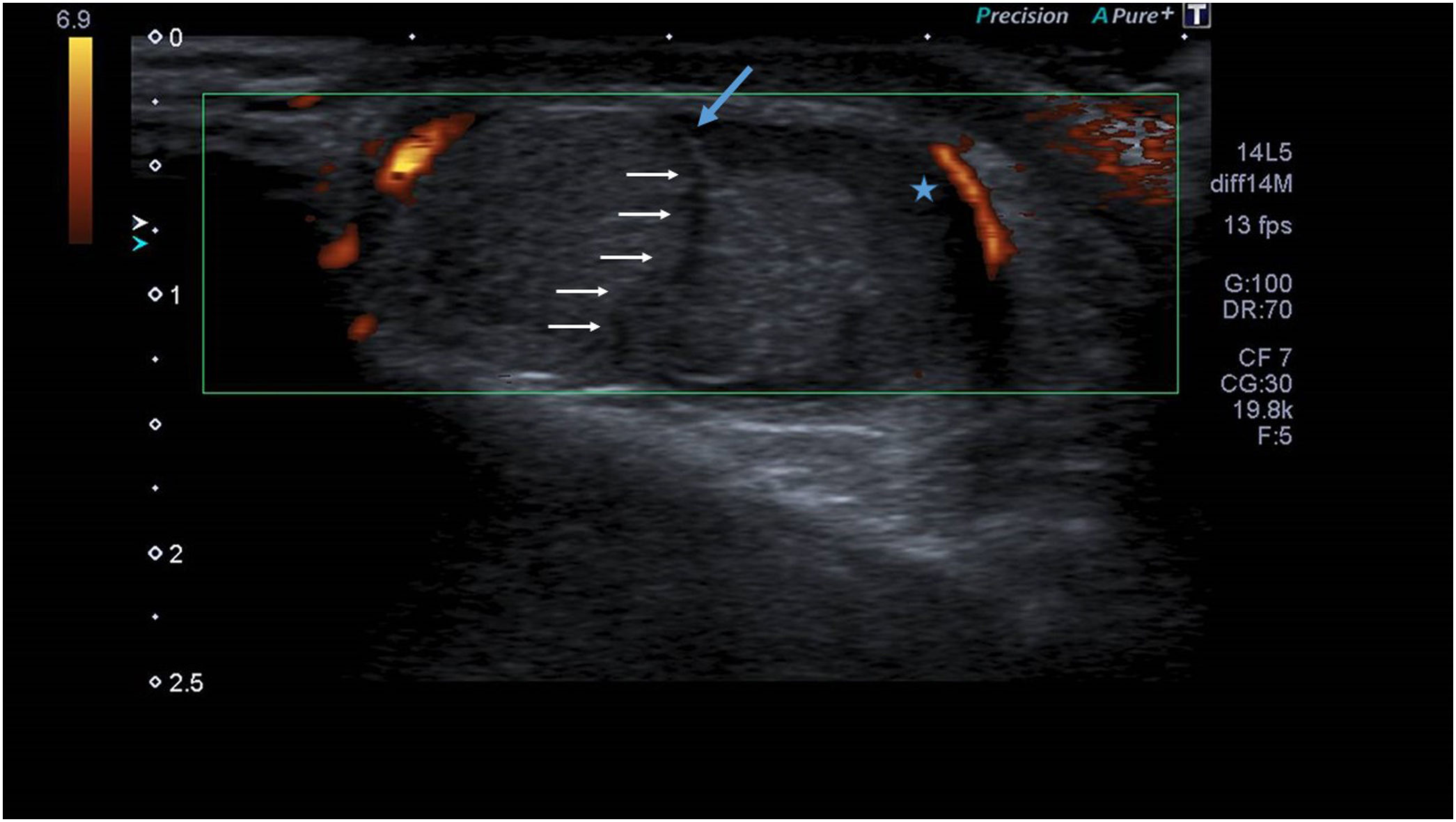
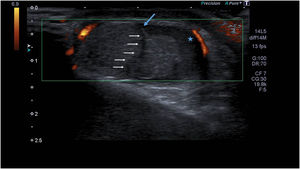
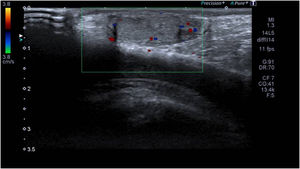
Preoperative ultrasound of the scrotum showing mild enlargement of the right testicle with heterogeneous echotexture in the parenchyma, contour abnormality and discontinuity of the tunica albuginea (blue arrow), absence of intratesticular fluid and haematocele (star). The white arrows point to the testicular rupture line.
Testicular and epidydimal rupture are infrequent. They usually occur following direct blunt trauma in the context of sports or a motor vehicle accident.1 Ultrasound of the scrotum is the imaging test of choice. Heterogeneous echotexture in the parenchyma and contour abnormality are highly sensitive and specific for diagnosis of testicular rupture.2 Early surgical repair has been found to achieve better outcomes compared to conservative management in terms of the preservation and function of testicular parenchyma, with a lower frequency of orchidectomy and greater comfort in the days following the traumatic injury.3