Cardiac arrest has a high mortality in children. To improve the performance of cardiopulmonary resuscitation, it is essential to disseminate the international recommendations and the training of health professionals and the general population in resuscitation.
This article summarises the 2015 European Paediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation recommendations, which are based on a review of the advances in cardiopulmonary resuscitation and consensus in the science and treatment by the International Council on Resuscitation. The Spanish Paediatric Cardiopulmonary Resuscitation recommendations, developed by the Spanish Group of Paediatric and Neonatal Resuscitation, are an adaptation of the European recommendations, and will be used for training health professionals and the general population in resuscitation.
This article highlights the main changes from the previous 2010 recommendations on prevention of cardiac arrest, the diagnosis of cardiac arrest, basic life support, advanced life support and post-resuscitation care, as well as reviewing the algorithms of treatment of basic life support, obstruction of the airway and advanced life support.
La parada cardiaca en niños tiene una elevada mortalidad. Para mejorar los resultados de la reanimación cardiopulmonar (RCP) es esencial la difusión de las recomendaciones internacionales de RCP y el entrenamiento de los profesionales sanitarios y la población general. Este artículo resume las recomendaciones europeas de RCP pediátrica de 2015, que están basadas en la revisión de los avances en RCP y el consenso en la ciencia y de tratamiento realizados por el Consejo Internacional de Resucitación. Las recomendaciones españolas de RCP pediátrica elaboradas por el Grupo Español de Reanimación Cardiopulmonar Pediátrica y Neonatal son una adaptación de las recomendaciones europeas y serán las utilizadas para la formación en reanimación a los profesionales sanitarios y la población general.
En el artículo se destacan los principales cambios con respecto a las anteriores del 2010 en prevención de la parada cardiaca, diagnóstico de la parada cardiaca, RCP básica, RCP avanzada y cuidados posresucitación, y se presentan los algoritmos de tratamiento de RCP básica, desobstrucción de la vía aérea y RCP avanzada.
Cardiac arrest (CA) in children carries a high morbidity and mortality. Research on cardiopulmonary resuscitation (CPR) is very complex,1–3 and advances come at a slow pace. Nevertheless, the outcomes of paediatric CPR have improved considerably with the diffusion of international CPR guidelines and the education of health care professionals and the general population.1–3
The International Liaison Committee on Resuscitation (ILCOR) reviews advances in CPR and develops the international Consensus on Science with Treatment Recommendations (CoSTR) every five years.4,5 The European Resuscitation Council develops its guidelines for resuscitation based on the CoSTR5–8 and assumes that the recommended strategiesneed to be adapted in each country.6 The Spanish paediatric CPR recommendations developed by the Spanish Group on Paediatric and Neonatal CPR are an adaptation of the European recommendations.5
This article summarises the 2015 paediatric CPR recommendations,4,5 emphasising the main changes from the previous recommendations.9
Cardiac arrest prevention- –
Identification of children at risk of CA: a significant percentage of children that experience CA do so following a period of clinical decompensation. Thus, early recognition of patient deterioration is crucial in reducing morbidity and mortality in seriously ill children.
- –
Action: in children at risk of CA, it is very important to follow a structured assessment and intervention scheme adhering to the following sequence: A (airway), B (breathing), C (circulation), D (disability/neurologic) and E (exposure). The child should be reevaluated frequently following this sequence.
- –
Organisation of CA care: each hospital must decide how to organise CA care based on its particular characteristics, taking into account that rapid response teams can reduce adverse events and improve outcomes associated with CA in hospitalised children.10
- –
Volume expansion: expansion is needed in cases of absolute or relative hypovolaemia (septic or anaphylactic shock). Although the solution used most frequently for initial expansion continues to be physiological saline solution, balanced crystalloids are less likely to lead tohyperchloraemic acidosis.11 The findings of a large-scale study in African children with febrile illness found that mortality was higher in patients that received a fluid bolus compared to patients that did not.12 Due to the potential risks in volume expansion, administration of a fluid bolus in children with febrile illness when circulatory failure is absent is currently not recommended.5
- –
Treatment of arrhythmias: in children with supraventricular tachycardia that do not respond to vagal manoeuvres and/or drugs and require electrical treatment (synchronised cardioversion), an initial dose of 1J/kg is recommended.5 The previous recommendation was an initial dose of 0.5J/kg.9
- –
Diagnosis of CA: palpation of a pulse is not reliable as the sole determinant of the need for chest compressions.13 Thus, in the absence of signs of life in the child, chest compressions should be initiated unless rescuers are certain that they can feel a central pulse within 10s.
- –
Echocardiography: echocardiography may help to detect cardiac activity and some potentially treatable causes of CA, but its use should not interfere with performance of CPR manoeuvres.
- –
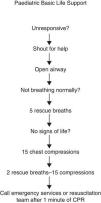
Basic life support (BSL) algorithm: Fig. 1 summarises the steps performed in basic paediatric life support. The manoeuvres are the same as those in the 2010 recommendations.5,9
- –
Sequence of actions: there is no evidence supporting the superiority of the CAB sequence (compressions, airway and breathing) over the ABC sequence (airway, breathing and compressions).4,14 Current European5 and Spanish recommendations maintain the ABC sequence, which is the one that has been taught thus far. Furthermore, the cause of CA in children is often respiratory, and thus ventilation is essential to recover from CA. Therefore, in children, after assessing and opening the airway, five initial rescue breaths followed by 1min of CPR should be performed before going for assistance.
- –
Duration of breaths: the recommended duration of delivering a breath in BSL is approximately 1s so that recommendations for children and adults in the general population coincide, facilitating learning.
- –
Compressions with rescue breathing versus compression-only: CPR with compressions and rescue breathing is superior to compression-only CPR.1 The recommendation for children with CA is to perform rescue breathing and chest compressions. Rescuers that do not know how to give rescue breaths may use compressions only, as this is preferable to doing nothing.
- –
Depth of compressions: in chest compressions, the sternum should be depressed by at least a third of the anterior-posterior diameter of the chest (approximately 4cm in infants and 5cm in children). However, assessing the depth of compression during CPR is very complicated. Some devices allow its measurement, but there is no evidence of their usefulness in guiding CPR in children.15
- –
Chest compression technique in infants: if there is only one rescuer, compression with two fingers perpendicular to the sternum facilitates the coordination of chest compressions and breaths. However, if at least two rescuers are present, the chest should be compressed with two hands using the encircling method, as it is more effective.
- –
Activation of emergency system: if a child becomes unconscious, it is vital to get help quickly. If only one rescuer is present, CPR should be performed for 1min before going for help. If there are at least two rescuers, one should initiate CPR while the other seeks assistance. A lone rescuer should only seek assistance first and then initiate resuscitation in the rare instance that the child suddenly collapses and the rescuer suspects primary cardiac arrest, as the child will likely need defibrillation.
- –
Automated external defibrillator (AED): CPR should never be discontinued to go seek an AED unless ventricular arrhythmia is suspected as the cause of CA and the AED is nearby and accessible. In children aged more than 8 years or weighing more than 25kg, the AED should be used with adult-size paddles. Paediatric paddles should be used in children aged 1–8 years (attenuated paddles delivering 50–75J). Adult pads should be used whenever paediatric paddles are not available.
- –
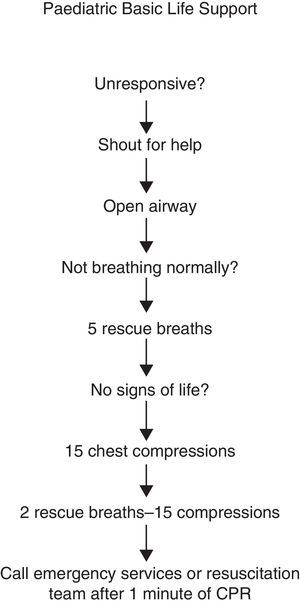
Foreign body airway obstruction (FBAO): there are no changes in the treatment recommendations (Fig. 2), as there has been no further research on this subject. Back blows, chest thrusts and chest compressions are used to try to increase intrathoracic pressure to push out the foreign body. If one of these measures is not effective, the others can be attempted on rotation until the object is cleared or the obstruction is relieved. However, rotating the three manoeuvres is difficult to learn, remember and implement in a life-threatening situation. For this reason, the Spanish Group on Paediatric and Neonatal CPR recommends rotating back blows and chest thrusts in infants, and back blows and abdominal thrusts in children in groups of five as long as the child remains conscious.
- –
The ABC sequence used in BLS should also be applied to advanced life support (ALS).
- –
Bag ventilation and supraglottic devices: bag-mask ventilation is the initial method used in airway management and ventilation during CPR in children. However, supraglottic devices (laryngeal mask and others) may be helpful in airway management when used by well-trained rescuers.
- –
Endotracheal intubation: cuffed tracheal tubes are as safe as uncuffed ones and reduce air leaks. However, an excessive cuff pressure can cause damage to the larynx and secondary stenosis. Thus, after the return of spontaneous circulation (ROSC), cuff inflation pressure should be monitored and maintained at less than 25cm H2O.
- –
Newly developed laryngoscopes: new laryngoscopes may facilitate complicated intubations if the rescuer is trained in their use, although there is still little evidence on their use in children.16
- –
Confirmation of tube placement: physical examination (chest wall movement and auscultation), vital signs and capnography can be used to confirm tube placement, but none of these methods is completely reliable. The presence of a capnographic waveform for more than four breaths is a good indicator of correct placement, but the absence of exhaled CO2 during CPR does not guarantee tube misplacement, as it may be due to reduced pulmonary blood flow. However, if the child is in CA and exhaled CO2is not detected despite adequate chest compressions, or there is any doubt as to the tube position, the placement of the tube should be confirmed by laryngoscopy.6
- –
Oxygen: when performing CPR in children, except in newborns, oxygen should be given at the highest possible concentration (100%), as hypoxia is more frequent and harmful than hyperoxiain this situation. Once there is ROSC, the fraction of inspired oxygen (FiO2) should be titrated to maintain SpO2 in the range of 94–98%.
- –
Respiratory rate: there are no reliable data to determine the most appropriate respiratory rate during CPR and after ROSC in children.
- –
Non-intubated patients: the European guidelines recommend using a ratio of 15 chest compressions to 2 breaths and a compression rate of 100–120 compressions per minute during BLS and ALS if the child is not intubated.
- –
Intubated patients: once the child is intubated, ventilation should be maintained at a rate of 10 breaths per minute without interrupting the chest compressions. Care should be taken to ensure that lung inflation is adequate during chest compressions.
- –
After ROSC: once ROSC has been achieved, normal ventilation (in rate and volume) should be provided based on the child's age and illness, and end-tidal CO2 and blood gases should be monitored to achieve normal PaCO2 and PaO2 values.
- –
Capnography: an end-tidal CO2 higher than 15mmHg may be an indicator of adequate resuscitation. However, the current evidence does not suffice to support the use of a specific threshold end-tidal CO2 value as an indicator for the quality of CPR, as a sign of return of spontaneous circulation or for the discontinuation of resuscitation.
- –
Vascular access: peripheral venous access is the access of choice, but it may be difficult to establish in children during CPR. Thus, if venous access cannot be attained within 1min, an intraosseous needle should be inserted and maintained only until definitive intravenous access is established. The tracheal route is not recommended for the administration of drugs unless no other route is available.
- –
Sodium bicarbonate: there is no evidence that supports the routine administration of sodium bicarbonate during CPR. Its administration can be considered in children with prolonged CA (for instance, lasting more than 10min) and/or severe metabolic acidosis.
- –
Atropine: atropine is only recommended for bradycardia caused by increased vagal tone or cholinergic drug toxicity. The most commonly used dose is 20μg/kg. In cases of bradycardia with poor peripheral perfusion unresponsive to ventilation and oxygenation, adrenaline is the first-line drug.
- –
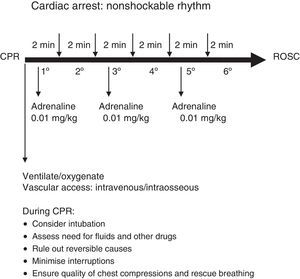
ECG monitoring: cardiac monitoring should be initiated as soon as possible. However, since most cardiac rhythms in children with CA are nonshockable, initial efforts should prioritise ventilation, chest compressions, establishing vascular access and administering adrenaline rather than wasting time searching for a monitor.
- –
The most common ECG patterns in children with CA are bradycardia, asystole and pulseless electrical activity.3,17 If a child with bradycardia (heart rate <60bpm in the absence of signs of life) does not respond quickly to ventilation with oxygen, chest compressions should be started immediately and adrenaline administered.
- –
Ventricular fibrillation and pulseless ventricular tachycardia are present in fewer than 20% of cases of CA in children. The incidence of shockable rhythms increases with age, and they are more likely to occur in children that collapse suddenly or with underlying heart disease.
- –
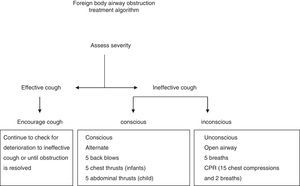
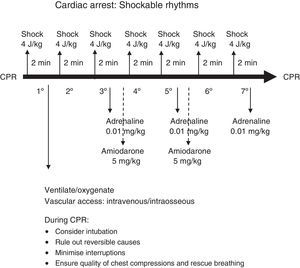
The algorithm for ALS is presented in Fig. 3, and the algorithms for nonshockable and shockable rhythms in Figs. 4 and 5.
- –
Defibrillators: manual defibrillators must be available in all health care facilities. If a manual defibrillator is not available, an AED may be used, as these devices can recognise shockable paediatric rhythms.18
- –
Defibrillation pads and paddles: self-adhesive pads facilitate CPR by reducing the time that chest compressions are discontinued to deliver the shock.
- –
Energy dose for electric shocks: in Europe, a dose of 4J/kg is still recommended for every shock.
- –
Antiarrhythmic drugs: administration of one 5mg/kg dose of amiodarone as a rapid bolus after the third shock is recommended, and can be repeated after the fifth shock. A recent study has reinforced that lidocaine may be useful in shockable rhythms in children.19 However, the European guidelines continue to recommend amiodarone as the drug of choice for shockable rhythms that do not respond to defibrillation. It must be kept in mind that during CA, amiodarone must be administered as a rapid bolus. Conversely, when amiodarone is administered to treat other cardiac rhythm disturbances in children that are not in CA, it must be injected slowly over 10–20min with systemic BP and ECG monitoring.20
- –
Table 1 provides a summary of the dosage of different drugs during paediatric CPR.
Table 1.Drugs used in paediatric life support.
Drug Dose Preparation Route Indication Adrenaline 0.01mg/kg
Max: 1mgDiluted in PS. (1+9)=0.1mL/kg
ET: undilutedIV, IO, ET
As bolusCA Adenosine 1. 0.2mg/kg
Max: 6mg
2. 0.4mg/kg
Max: 12mgQuickly flush after administration with 5mL of PS IV, IO as bolus SVT Amiodarone 5mg/kg
Max: 300mgPure IV, IO
As bolus in CA
Slow infusion otherwiseRefractory VF or PVT
SVT o TVAtropine 0.02mg/kg
Max: 1mgDiluted in saline (1+9)=0.2mL/kg IV, IO
As bolusVagal bradycardia Bicarbonate 1mEquiv./kg
Max: 50mEquiv.Diluted 1:1 with PS=2mL/kg IV, IO
As bolusRefractory CA Calcium 0.2mEquiv./kg =
Max: 10mEquiv.Calcium gluconate 10% 0.4mL/kg
Calcium chloride 10% 0.2mL/kg 1:1 dilutionIV, IO lento Hypocalcaemia, hyperkalaemia, hypermagnesaemia
Calcium channel blocker toxicityGlucose 0.2–0.4g/kg Glucose 10%
=2–4mL/kgIV, IO
As bolusDocumented hypoglycaemia Lidocaine 1mg/kg
Max: 100mgUndiluted IV, IO
As bolusRefractory VF or PVT Fluids 20mL/kg PS IV, IO
RapidPEA
HypovolaemiaMagnesium 50mg/kg Undiluted IV, IO
As bolusPolymorphic VT
With torsades de pointesCA, cardiac arrest; ET, endotracheal; IO, intraosseous; IV, intravenous; Max, dose maximum; PEA, pulseless electrical activity; PS, physiologic saline; PVT, pulseless ventricular tachycardia; SVT, supraventricular tachycardia; VF, ventricular fibrillation.
- –
Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO): the use of ECMO can be considered in children with CA due to a potentially reversible cause and refractory to conventional CPR if the child is in a facility with the necessary resources, trained staff and organisation allowing for quick initiation of ECMO.
- –
Life support in trauma patients: cardiac arrest from major trauma is associated with a high mortality. Resuscitation in these patients does not differ from the routine management of CA from other causes, although the use of resuscitative thoracotomy can be considered in children with penetrating injuries.
- –
Pulmonary hypertension: children with pulmonary hypertension are at increased risk of CA. These patients should be managed with a high FiO2, alkalosis and hyperventilation, which may be as effective as inhaled nitric oxide in reducing pulmonary vascular resistance.21
- –
Coordinated care: Postresuscitation care must be a coordinated multidisciplinary activity and include all the treatments needed for complete neurologic recovery.
- –
Haemodynamic treatment: treatment must be adjusted to maintain a systolic blood pressure above the 5th percentile for age. After resuscitation, it is important to avoid hypotension, as this factor is associated with significantly worse outcomes.22
- –
Oxygenation and ventilation: once the child is stabilised, management must aim for a normal PaO2 range. There is insufficient evidence to suggest a specific PaCO2 target after ROSC in children, and both hypocapnia and hypercapnia are associated with a poor prognosis.23Aiming for normocapnia is recommended, adapting to the needs of each patient.5 Therefore, it would be appropriate to initiate ventilation with a normal rate and volume, adjusting them to the child's age and illness, while monitoring end-tidal CO2and blood gas levels.
- –
Temperature: the THAPCA study did not find significant differences in neurologic status at one year from CA between children treated with hypothermia and children treated with normothermia.24 On the other hand, fever after ROSC has been associated with a poorer prognosis.25 Therefore, the current recommendation is to keep a strict control of temperature after ROSC, preventing both hyperthermia (>37.5°C) and severe hypothermia (<32°C), maintaining the patient in normothermia or mild hypothermia.
- –
Glucose: glucose levels must be monitored after resuscitation, avoiding hyperglycaemia and hypoglycaemia, as both are associated with impaired outcomes.
- –
Prognosis of CA: the duration of CPR, the cause of arrest, pre-existing medical conditions, age, site of arrest, whether the arrest was witnessed, the duration of untreated CA, the presence of a shockable rhythm and special circumstances such as icy water drowning or exposure to toxic drugs are significant prognostic factors in children with CA.1,5 However, there is no single reliable predictor of outcome after CPR. In adults, a multidisciplinary approach combining physical examination, electroencephalography, electrophysiology, imaging tests and biomarkers can guide prognostication starting at 72h after ROSC.26
- –
Parental presence: in some countries, parents often want to be present while CPR is performed on their children, which facilitates the grieving process. However, evidence on this subject cannot be generalised to all of Europe, where there may be different sociocultural characteristics. Therefore, parental presence will depend on the characteristics of both the parents and the resuscitation team.27
RETICS funded by Spain's PN I+D+I 2013-2016 (National Plan for Scientific Research, Development and Innovation), Instituto de Salud Carlos III – Sub-Directorate General for Research Assessment and Promotion and the European Regional Development Fund (ERDF), ref. RD16/0022.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: López-Herce J, Rodríguez A, Carrillo A, de Lucas N, Calvo C, Civantos E, et al. Novedades en las recomendaciones de reanimación cardiopulmonar pediátrica. An Pediatr (Barc). 2017;86:229.