Accidents in the paediatric population are an important issue due to both their high frequency and their potential impact on health, and they are the leading cause of death in children aged more than 1 year.1,2 Families, schools and the government are essential agents in providing minors with safe environments, promoting the development of skills to manage risks successfully and enacting regulations aimed at preventing accidents in this age group.
Royal Decree 989/2015, of 30 October in Spanish law, which regulates fireworks, ammunition and explosives, establishes 8 types of pyrotechnic products, of which only those in categories F1, F2 and F3 can be used for recreational purposes.3 Products in category F1 are considered to present very low hazard and may be used by individuals aged 12 years or older, those in category F2 are considered a low hazard and may be used by individuals aged 16 years or older, and those in category F3 are considered a medium hazard and can only be used by adults aged 18 years or older. Regional regulations at the autonomous community level4 lower the age established at the national level to as young as 8 years for category F1 and 10 years for category F2, although in every case current regulation prohibit the sale and purchase of firecrackers to children aged less than 12 years. For age reductions to be applicable, a written authorization by the parents or legal guardians is required. This authorization does not need to be filed with any governmental agency, but it must be carried by the child at all times.
The aim of the study was to describe the characteristics of firework-related accidents managed in the paediatric emergency department of a tertiary care hospital in an autonomous community with a lower age limit for the use of pyrotechnic products.
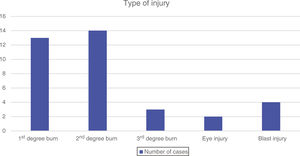
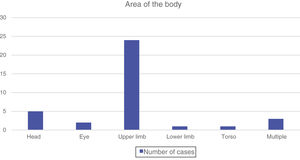
Between January 2014 and December 2018, 36 children aged less than 15 years sought care for firework-related injuries, with most cases clustered around the week of local festivities. The mean age of the patients was 8.7 years (standard deviation, 3.66; median, 9 years; range, 1–14 years), and 63.89% were male. Of the total cases, 38.8% occurred in children aged less than 8 years, revealing noncompliance not only with nationwide policy but also regional policy. In most cases (91.6%) the accident took place in the afternoon or evening in the context of local festivities. The patients did not exactly specify the type of pyrotechnic product that caused the injury, although the hazardous potential of the products was evinced by the injuries managed: eye injuries, burns and blast injuries (Fig. 1). We were unable to determine whether the patients were accompanied by an adult and had the appropriate authorization at the time of the accident.
Second degree burns in the right hand were the most frequent type of injury (66.6%), which indicates that the accident occurred during handling of the product (Fig. 2). There were 3 cases of third-degree burn and 4 severe injuries (11.1%) with loss of tissue, fracture and need of surgery and grafting, in a girl aged 1 year injured during a fireworks show and 3 boys aged 10 years injured during handling of a product. In 19.4% of the patients, the injuries required referral to the regional burn centre.
Pyrotechnics should not be considered toys, but devices that may cause serious injuries and burns. The American Academy of Paediatrics recommend a complete ban on the use of fireworks by children.5 The European Child Safety Alliance recommends never to let children play with fireworks due to the risk of injury. As is the case of Spain, all member states of the European Union have laws regulating or even banning the sale of fireworks to children and their use by children, which have had a positive impact as evinced by a decrease in the number of related accidents.6
In our sample, most children suffered the injury while handling the product, and had a mean age that was lower compared to previously published case series,7 which suggests a lack of direct supervision and noncompliance with regulations that are already lax. Our findings, based on data from a region where there is a tradition in the use of fireworks, may not be representative of other regions in Spain. Pyrotechnic products must be used responsibly and in adherence with current regulation, so that they can be enjoyed while avoiding accidents.
Please cite this article as: Sebastián Cuevas FJ, Lázaro Carreño MI, Barrés Fernández A, Noguera Carrasco S, Angelats CM. Impacto de la normativa autonómica para la prevencion de accidentes pirotécnicos. An Pediatr (Barc). 2020;93:415–417.
Previous presentation: this study was presented as a communication at the 24th Meeting of the Sociedad Española de Urgencias Pediátricas (SEUP); May 10, 2019; Murcia, Spain.