Alopecia areata is a non-scarring, chronic, and inflammatory hair loss disease with a low prevalence in the pediatric population. There is evidence of an association with several autoimmune disorders, such as Hashimoto disease, and several triggers, such as stress.1 However, there is a dearth of data on its association with nephrotic syndrome.2 The pathogenesis of both alopecia areata and nephrotic syndrome involves immune dysregulation.2 There are local treatments that stimulate hair growth and systemic treatments that modify the course of disease, such as Janus kinase (JAK) inhibitors.3 At present, the only JAK inhibitors authorized for this indication are ritlecitinib and baricitinib.
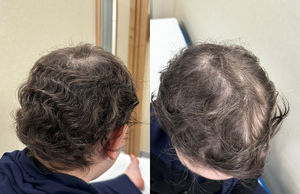
We present the case of a female adolescent aged 13 years with steroid-resistant nephrotic syndrome with onset at age 3 years. The patient received immunosuppressive therapy with oral prednisone, tacrolimus and mycophenolate mofetil. At age 11years, she developed an alopecia areata patch, which was treated locally with minoxidil and steroids, which was not successful, with progression to alopecia totalis (Fig. 1) and, later on, to alopecia universalis. Since her renal condition was stable, the patient started treatment with tofacitinib (a JAK inhibitor that has been found effective for management of alopecia areata), since the drug was available in the hospital, with progressive increase of the dose until reaching 5mg every 8h and discontinuation of mycophenolate mofetil. Four months later, there was evidence of incipient hair growth, with full regrowth of the eyebrows and significant regrowth on the scalp by 1year of treatment (Fig. 2). The patient has not experienced nephrotic syndrome relapse since the initiation of tofacitinib.
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.




![Condition prior to initiation of treatment with tofacitinib: alopecia totalis (Severity of Alopecia Tool [SALT] score, 30). Subsequent progression to alopecia universalis.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/23412879/0000010300000001/v2_202510131241/S2341287925002303/v2_202510131241/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w95erwEulN6Tmh1xJpRhO+VE=)