After birth, it is the duty of the paediatrician to provide education on breastfeeding, newborn care and safety and warning signs of disease, in addition to promoting follow-up of the child at the outpatient level.1 Clinical guidelines recommend a newborn check-up visit at the primary care level in the first 48–72h following discharge.2,3
The published evidence on the quality of the care delivered in maternity wards in Spain and the follow-up of newborn infants following hospital discharge is scarce.4,5 We designed a study with the primary objective of assessing adherence with the recommended post-discharge follow-up of the newborn infant in which we also assessed the satisfaction with the care received as a secondary objective.
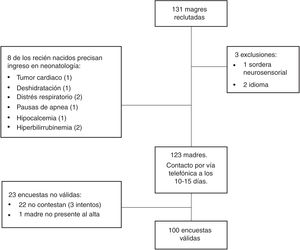
We conducted a cross-sectional observational study through telephone interviews held 10–15 days post partum with mothers discharged from the department of neonatology of a tertiary care hospital between April 2018 and April 2019. We obtained the sample by seeking informed consent from mothers on days allotted to recruitment based on the availability of the researchers. The questionnaire used in the interview, designed by the researchers, included items on demographic characteristics, infant feeding and visits to the primary care centre and emergency department. Six items were devoted to the satisfaction of participants with different care-related aspects, such as the quality of customer service, professional competence, the clarity of explanations and the thoroughness of the information provided regarding medical care after discharge, all of which were rated on a Likert scale.
We performed a descriptive and bivariate analysis, comparing means and proportions, and a multivariate analysis by means of generalised linear models. We considered P-values of less than .05 statistically significant. The study was approved by the Clinical Research Ethics Committee of the hospital.
We analysed data corresponding to 100 telephone interviews (Fig. 1). Eighty-four percent of newborn infants had attended a check-up visit in the first 15 days post birth and 66.7% in the first 72h post discharge. Eleven percent had not had a paediatric visit at the time of the interview and 4% had not visited the primary care centre. In 64.6% of cases, the first visit corresponded to the first routine check-up scheduled in the official healthy child programme.
Nineteen percent of respondents had made a visit to the paediatric emergency department before 15 days post birth, none of them resulting in hospital admission, and the most frequent reasons for emergency visits were concerns regarding newborn care (52.6%) and jaundice (36.8%).
The only factor significantly associated with increased adherence with the recommendation to attend a checkup post discharge (Table 1) was a high level of satisfaction with the detailed information about newborn care provided at discharge, with a weak to moderate strength of association (Cramer V, 0.214; P=.03), that was confirmed in the logistic regression analysis (odds ratio, 0.28; 95% confidence interval, 0.09−0.84; P=.02).
Characteristics of newborn infants and their mothers based on whether they had adhered to the recommendation of visiting the primary care centre in the first 72h post discharge or 6 days post birth.
| Visit to PCC within 6 days | Visit to PCC after more than 6 days | P | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 64 | 32 | |
| GA (weeks) | 40.0 (IQR, 38.8−40.7) | 39.5 (IQR, 38.6−40.5) | .26 |
| BW (grams) | 3313.9 (SD, 443.1) | 3273.7 (SD, 416.5) | .67 |
| % weight loss | 6.0 (IQR, 5.0−7.5) | 5.7 (IQR, 3.0−8.2) | .57 |
| Feeding modality at discharge | 39% (39) | 22% (22) | .26 |
| Exclusive or mixed BF | 25% (25) | 10% (10) | |
| AF | |||
| Maternal age (years) | 35.0 (IQR, 31.0−38.0) | 35.5 (IQR, 31.2−39.0) | .38 |
| Educational attainment | .28 | ||
| Primary education | 11% (11) | 10% (10) | |
| Secondary education | 15% (15) | 7% (7) | |
| University degree | 38% (38) | 15% (15) | |
| First child | 35% (35) | 20% (20) | .47 |
| Discharge in the weekend | 9% (9) | 6% (6) | .55 |
| BF support group | 4% (4) | 7% (7) | .82 |
| Emergency visit | 15% (15) | 4% (4) | .21 |
| Satisfied with detailed information provided at discharge (rated 4 or 5 on Likert scale) | 46% (46) | 29% (29) | .03 |
AF, artificial formula; BF, breastfeeding; BW, birth weight; GA, gestational age; IQR, interquartile range; PCC, primary care centre; SD, standard deviation.
We found large proportions of respondents who expressed high levels of satisfaction in every item in the questionnaire (ratings of 4 or 5): 99% highly satisfied with customer service (mean, 4.77; standard deviation [SD], 0.44); 88% with the information regarding medical care after discharge (mean, 4.46; SD, 0.73); 100% with the caring/kindness (mean, 4.89; SD, 0.31) and professional competence (mean, 4.83; SD, 0.37) exhibited by the paediatrician; and 79% with the thoroughness of the information provided on specific aspects of infant care (umbilical cord care, hygiene, feeding, sleep), with a mean rating of 4.28 points (DE 0.88).
The most salient finding of our study was that one third of newborn infants had not attended the initial checkup within the recommended timeframe. The only factor significantly associated with adherence to this recommendation was the level of satisfaction with the thoroughness of the information provided at discharge, which highlights the crucial role of the neonatologist in improving follow-up after discharge. Scheduling the appointment before discharge1 and receiving a consistent message from every health care professional are some of the factors that could reduce the impact of administrative barriers and improve adherence.5
In our study, we found a higher frequency of emergency department visits compared to the previous literature,6 but not associated with an increased frequency of hospital admission. The lower ratings given to the thoroughness of the information on infant care provided at discharge may have contributed to concerns regarding infant care being the most frequent reason for visiting the emergency department.
The main limitations of our study were the small sample size and the use of a questionnaire that has not been validated. We also did not explore potential administrative or logistic barriers that may hinder the follow-up of newborn infants. It may be useful to ensure that the entire health care staff provides consistent information at the time of discharge, preferably in writing.
In conclusion, our study found that the proportion of adherence with the current recommendation needs to improve and that parental satisfaction with having received detailed information from the paediatrician at the time of discharge is a strong determinant of adherence.
FundingThis study did not receive any form of funding.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Castro Rodríguez C, González Roca I, Marsinyach Ros MI, Sánchez Luna M, Pescador Chamorro MI. Encuesta de satisfacción sobre atención hospitalaria tras el nacimiento y segui-miento al alta del recién nacido sano. An Pediatr (Barc). 2021;95:197–199.
Previous presentation: This study was presented at the biannual Congreso de Neonatología y Medicina Perinatal, XXVII Edition; October 2–4, 2019; Madrid, Spain.